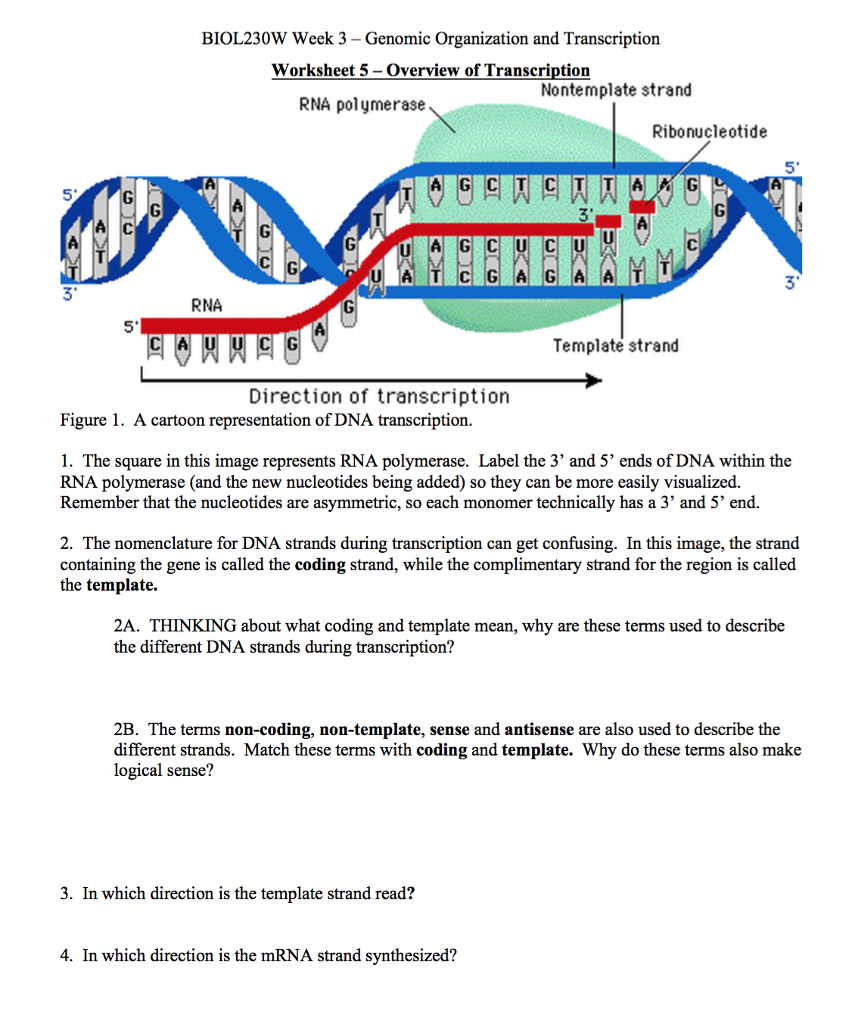
Dna Polymerase Reads The Dna Template Strand From The

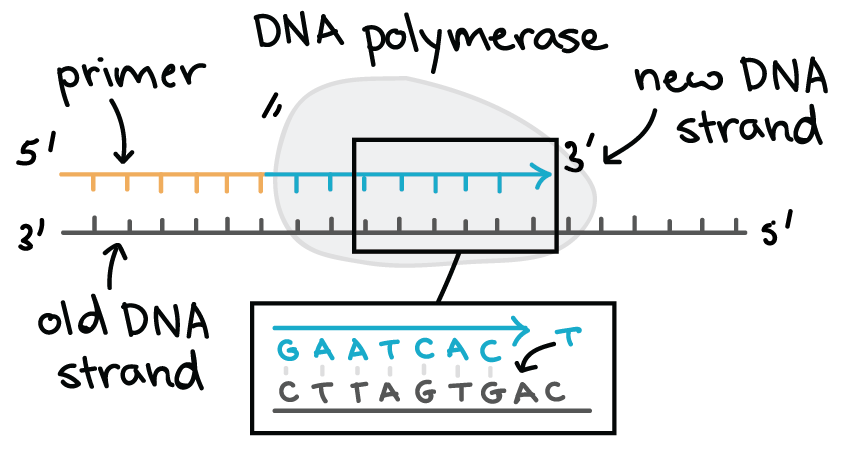
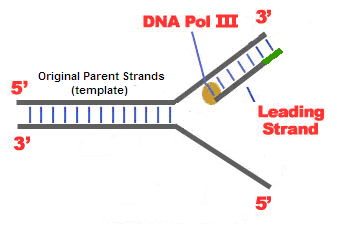
Since dna polymerase requires a free 3 oh group for initiation of synthesis it can synthesize in only one direction by extending the 3 end of the preexisting nucleotide chain.
Dna polymerase reads the dna template strand from the. Modification that must be made to the rna transcript on the 5 end prior to translation in eukaryotic cells. Because a t bonds are weaker than c g bonds the double helix opens up at this point and rna polymerase begins translation. A tiny amount of rna is needed to tell the cell where genes are located. Only half of it is old.
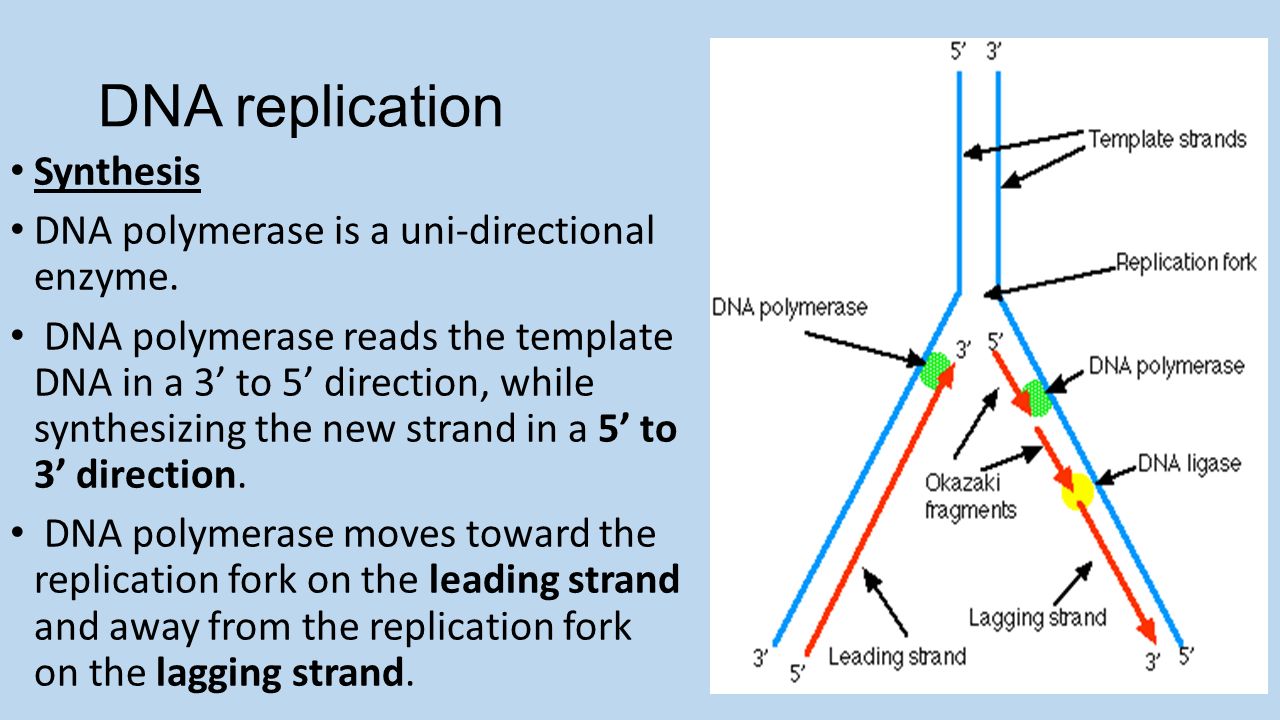
Dna polymerase can only add nucleotides to an existing chain. Dna polymerase adds nucleotides in 5 3 direction but this leaves gap in the lagging strand so dna ligase seals gaps on the lagging strand why is dna replication semi conservative because when two double helixs form each one has a single strand of the old and one from the new strand of dna. The primers help with the proofreading function of dna polymerase. Dna polymerase 3 comes in and reads the genetic sequence of the dna creating a complimentary base pair.
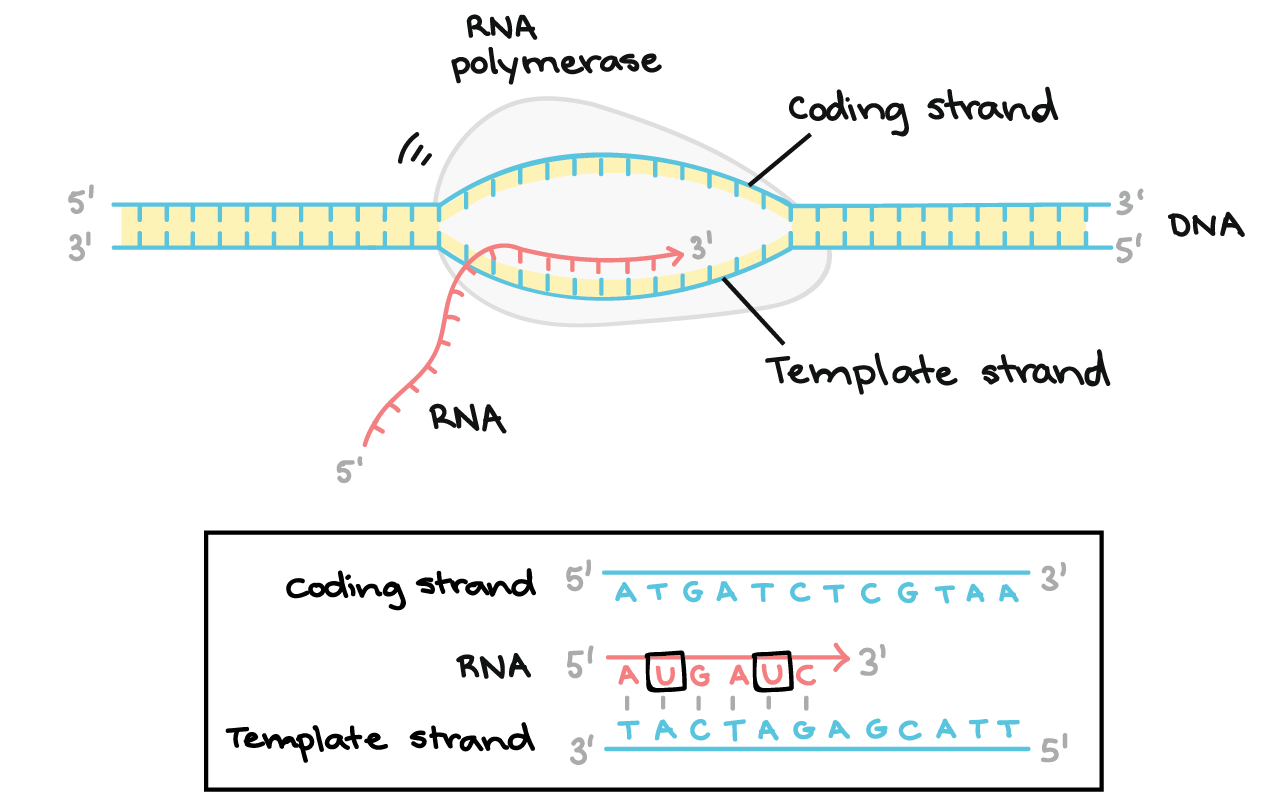
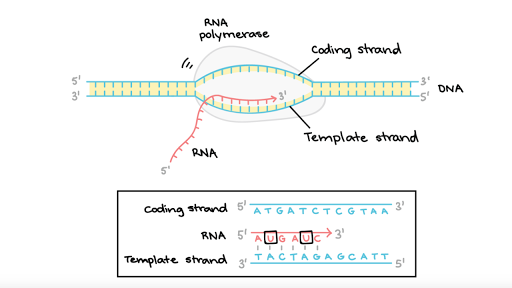
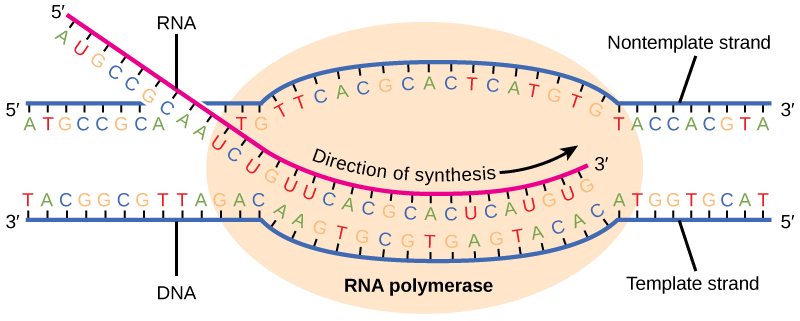
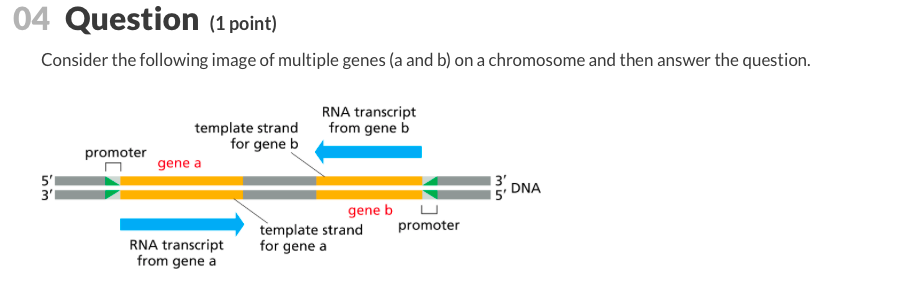
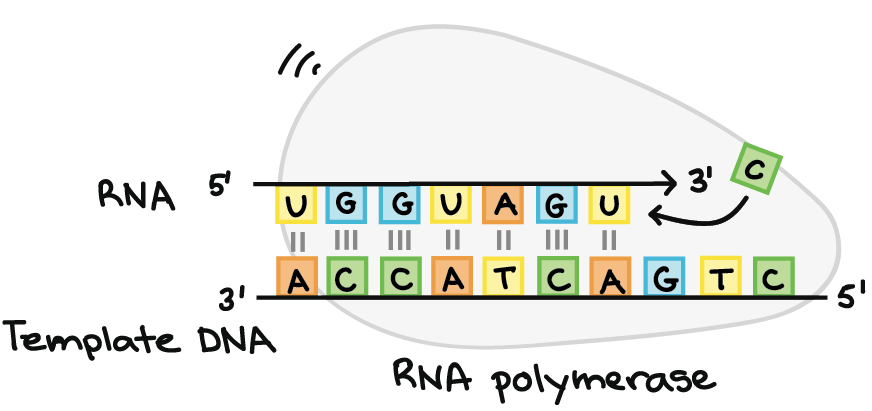
First rna polymerase binds to an a t rich promoter on the dna which is upstream from the site of translation. The template strand dna is read by rna polymerase in the 3 5 direction. It builds a new strand from 5 to 3 by moving along the template strand and pushing the replication fork ahead of it. Modification that must be made to the rna transcript on the 3 end prior to translation in eukaryotic cells.