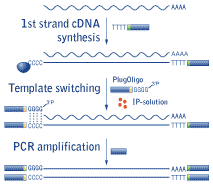
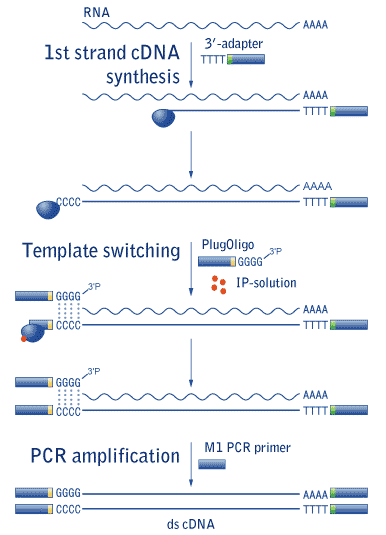
Template Switching Reverse Transcriptase

Template switching polymerase chain reaction ts pcr is a method of reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction pcr amplification that relies on a natural pcr primer sequence at the polyadenylation site also known as the polya tail and adds a second primer through the activity of murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase.
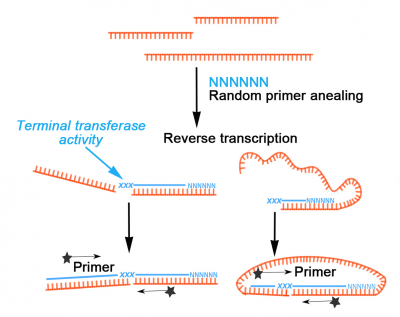
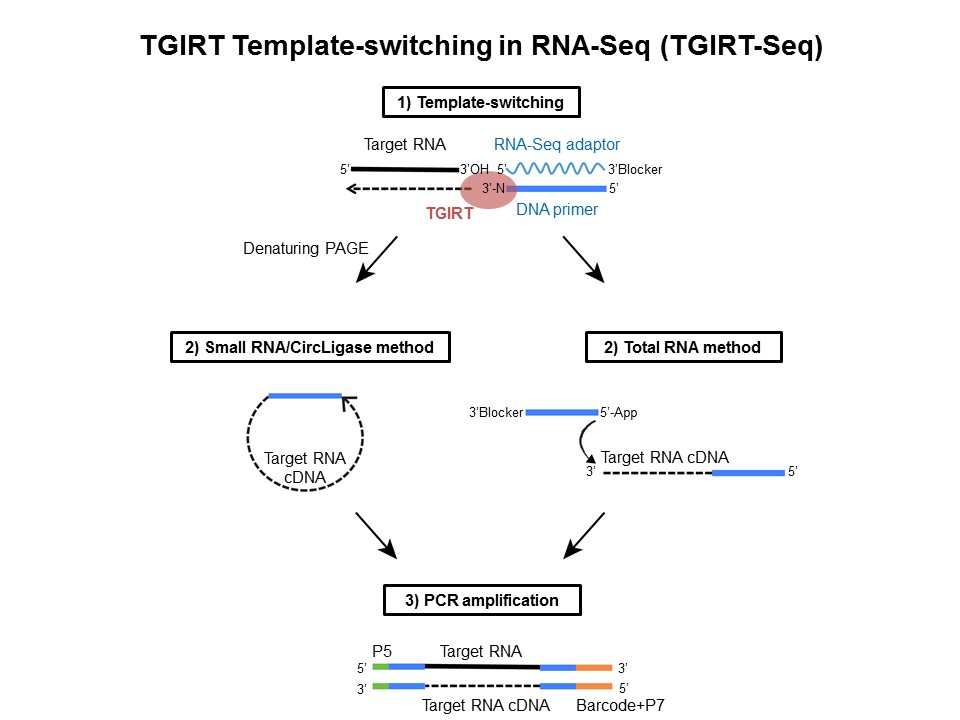
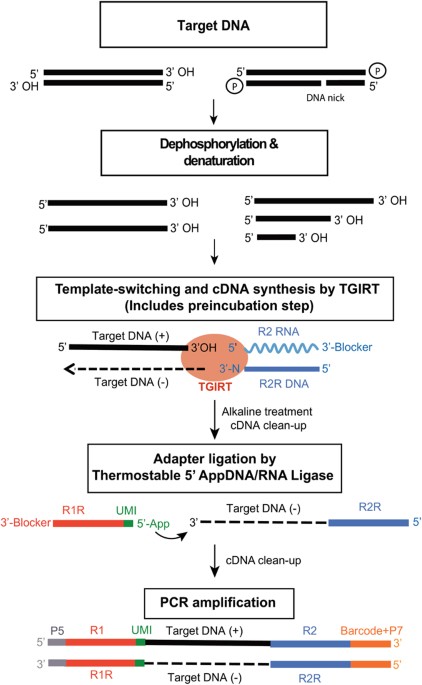
Template switching reverse transcriptase. Rt undergoes frequent additional switches of templates leading to a great variability in retroviral populations. The reverse transcriptase rt in the template switching rt enzyme mix adds a few non templated nucleotides after it reaches the 5 end of the rna template. The ability of reverse transcriptase to make template switches during dna synthesis is implicit in models of retrovirus genome replication as well as in recombination and oncogene transduction. 1 this template switching activity greatly facilitates strand specific rna seq library construction with less bias than procedures employing random hexamer primer or using rna ligase for adapter ligation.
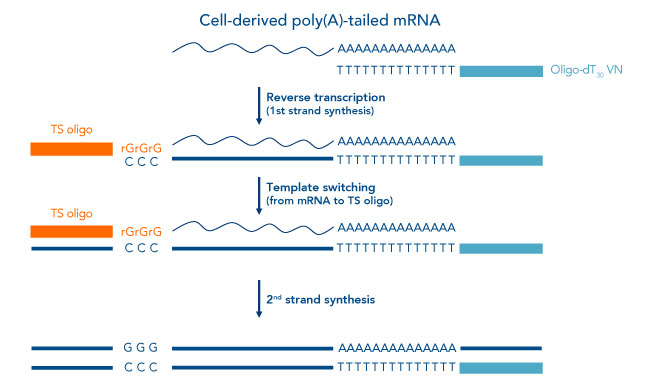
Template switching is believed to happen in a sequential process involving non templated addition of three protruding nucleotides ccc to the 3 end of the nascent cdna which can then anneal to the matching rgrgrg 3 end of the template switching oligo tso allowing the reverse transcriptase rt to switch templates and continue copying the tso sequence. In order to understand such switching we used in vitro reactions with purified nucleic acids and enzymes. Based on several studies usi. During reverse transcription of a retroviral genome reverse transcriptase rt enzyme must undergo two template switching events which occur at the ends of the template to complete dna synthesis.
Novel end to end template switching activity that enables attachment of rna seq or pcr adapters during reverse transcription and eliminates the need for a separate tailing or rna 3 adapter ligation step. The tso template switch oligo is an oligo that hybridizes to untemplated c nucleotides added by the reverse transcriptase during reverse transcription. These template switching ts events are generated in a homology dependent manner. Reverse transcriptases rts frequently switch templates leading to an increase in genetic variation and retroviral recombination.
Upon base pairing between the ts oligo and the appended deoxycytidine stretch the reverse transcriptase switches template strands from cellular rna to the ts oligo and continues replication to the 5 end of the ts oligo.